Plant morphology
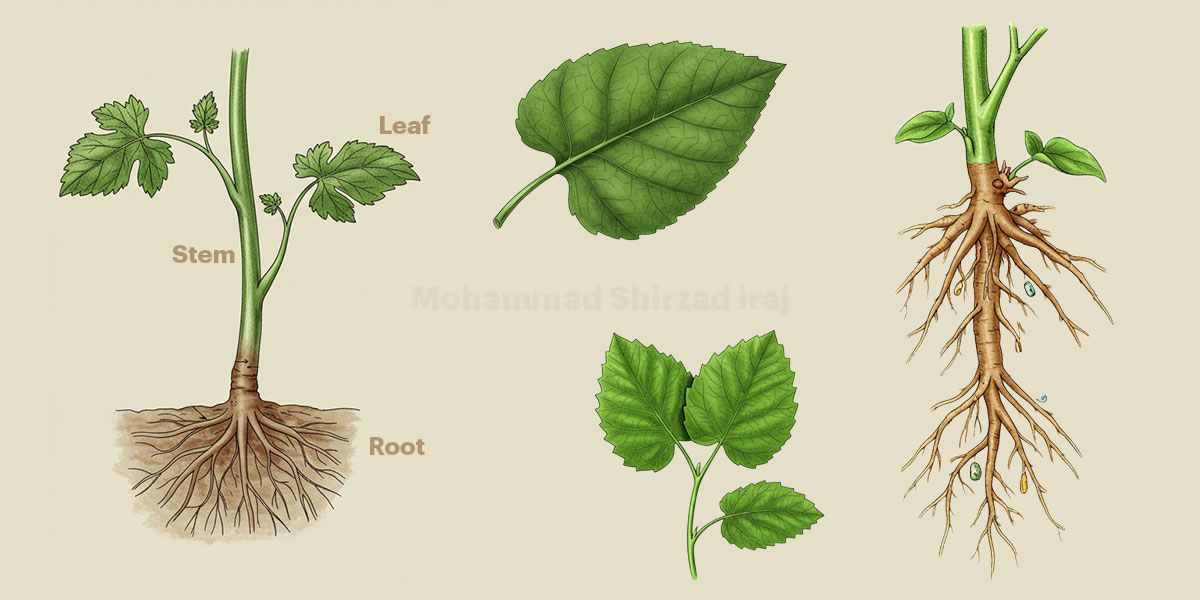
Vegetative morphology
Root , Stem , Leaf
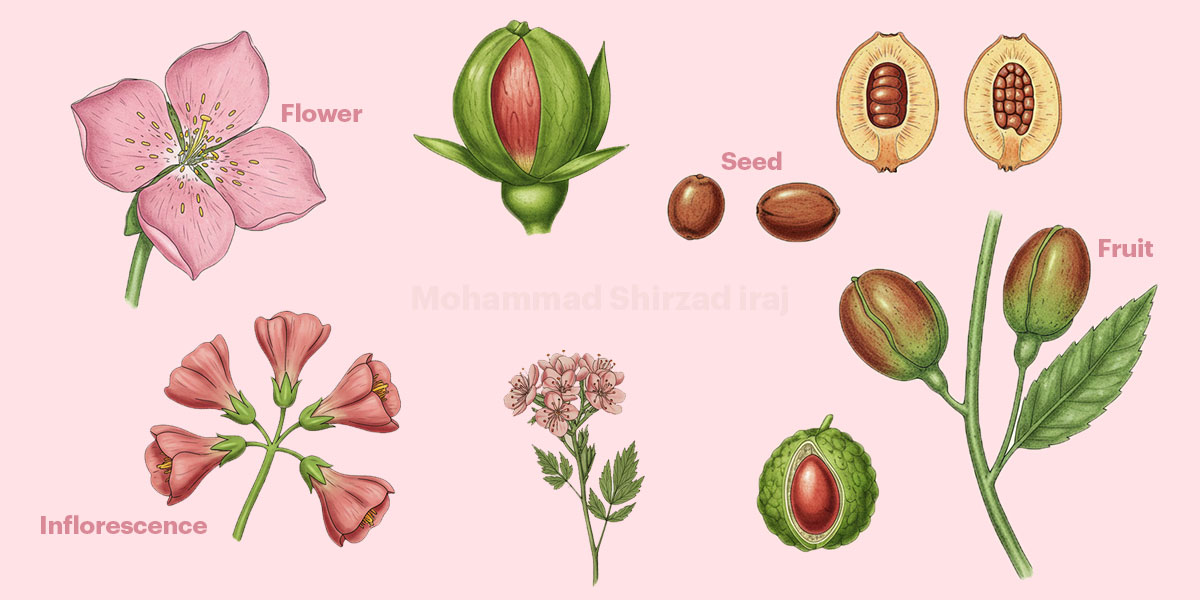
Reproduction morphology
Flower , Inflorescence , Fruit , Seed
Plant Morphology
✅ Plant Morphology
Plant morphology is a branch of botany that deals with the study of the external structure and form of plants throughout their life cycle. It focuses on the shape, size, organization, and arrangement of plant organs, and how these traits vary across different plant species. Morphological studies are essential for plant identification, classification, understanding adaptation, and analyzing evolutionary patterns.
There are two major subdivisions of plant morphology:
- Vegetative Morphology, which deals with the structural organization of the plant body involved in growth and maintenance.
Reproductive Morphology, which focuses on the organs and structures responsible for reproduction and the production of seeds.
🌿 Vegetative Morphology
Vegetative morphology refers to the study of non-reproductive (asexual) plant organs, primarily responsible for maintaining the plant’s life processes such as absorption, support, transport, and photosynthesis. These organs include the root, stem, and leaf.
1. Root: The root is an underground organ that anchors the plant in the soil, absorbs water and mineral nutrients, and sometimes functions in storage of food or vegetative propagation.
2. Stem: The stem is the main aerial axis of the plant that supports leaves, flowers, and fruits. It also serves as a conduit for the transport of water, minerals, and food between the root and other parts of the plant.
3. Leaf: The leaf is typically a flat, green organ arising laterally from the stem. It is the main site for photosynthesis, gas exchange, and transpiration in most plants.
🌸 Reproductive Morphology
Reproductive morphology focuses on the study of plant organs that are directly involved in sexual reproduction. These organs are responsible for the formation of gametes, fertilization, and the development of seeds and fruits. The key reproductive structures are the flower, inflorescence, fruit, and seed.
4. Flower: The flower is the reproductive unit of angiosperms (flowering plants) that contains male (androecium) and/or female (gynoecium) reproductive organs. It facilitates pollination and fertilization.
5. Inflorescence: An inflorescence is the arrangement or grouping of multiple flowers on a stem or floral axis. It affects the efficiency of pollination and seed production.
6. Fruit: The fruit is a mature ovary that develops after fertilization. It contains seeds and often aids in their protection and dispersal.
7. Seed: The seed is the fertilized and matured ovule containing the embryo, a food reserve, and a protective seed coat. It serves as the unit of reproduction and propagation in seed plants.